Yellow may be the new “it” colour in today’s fashion scene. In fact, “Yellow is the new black,” they say, and many would add pops of bright, whimsical yellow to their wardrobe.
But, in the realm of health and medicine, the colour yellow might be a telling sign of a health sorrow – jaundice.
To learn more about this health condition, let’s hear from Consultant Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist at Beacon Hospital, Dr P. Rajesh Kumar.
“Jaundice is a condition typified by yellowish skin and the whites of the eyes becoming yellow, too.” said Dr Rajesh during a webinar on jaundice.
Indeed, jaundice comes to the surface when the level of bilirubin in our body is higher than usual, which is over 40 micromol per litre.
Bilirubin is a yellow substance that originates from the breakdown of red blood cells aka haemoglobin, which is made up of two components: heme and globin. When heme is broken down by the liver, bilirubin is produced.
Bilirubin, when metabolised, gives your urine and stool those colours (well, you know). However, as mentioned earlier, if the level of bilirubin in your body skyrockets, as is evidenced by the yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes, underside of the tongue, dark urine and more, it means you may have gotten jaundice, and that a check-up may be the best next step.
First things first, we have to understand how does the normal flow of bilirubin work.
As the liver secretes bilirubin, it enters the gall bladder, which is a pear-shaped pouch situated just beneath the liver. The gall bladder stores the bilirubin for safekeeping, so to speak, and only releases it out when it’s needed. Once it’s released, it goes into the duodenum (first part of the small intestine) through the bile duct, which eventually merges with the nearby pancreatic duct to form a common tract. The small intestine is where the food we eat is channeled to.
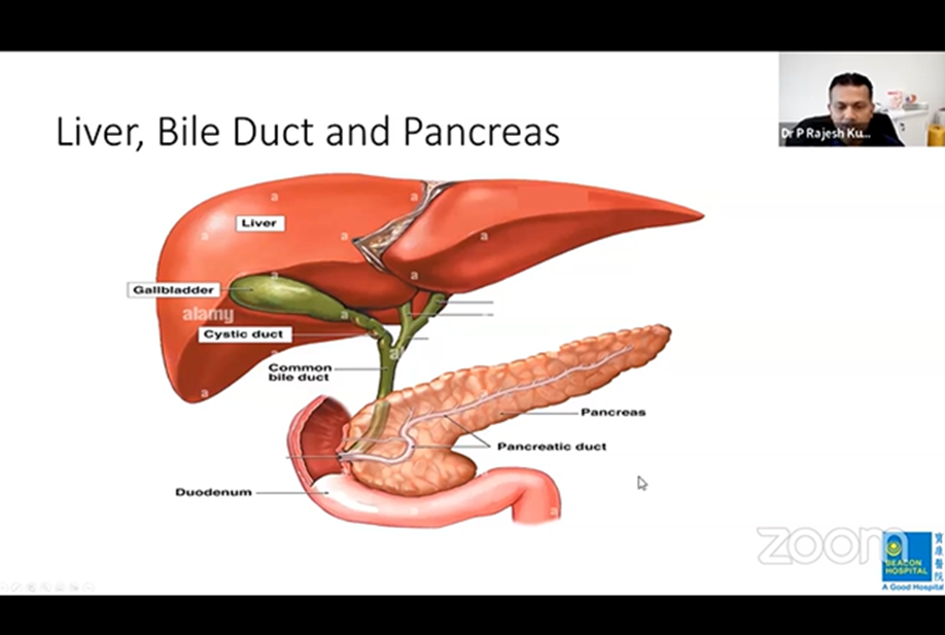
The normal flow of bilirubin from the liver to the duodenum / small intestine, as explained by Dr Rajesh in a Zoom webinar
Any blockage, disruption, or damage to this flow will cause the amount of bilirubin to go sky-high and in turn, causes jaundice. How? Dr Rajesh has given us a pretty relatable real-life analogy to help us understand further.
“It’s akin to the toll gate system.” quipped Dr Rajesh.

The causes of jaundice can be explained using the toll gate analogy, said Dr Rajesh
Imagine this: when heavy traffic goes through the toll gate, then, as expected, there will be congestion; likewise, when a heavy amount of bilirubin goes through the liver, the bilirubin level rises. On the other hand, if the toll gate is faulty, traffic can build up, too. In the context of jaundice, this is like having a faulty liver that will cause bilirubin to surge abnormally as well. Besides, if an accident happens after the toll gate, the traffic will no doubt turn bad, which, in this case, is equivalent to the increase in bilirubin due to problems in the bilirubin flow after the liver.
As a matter of fact, problems that occur before, at, and after the toll gate do strike parallels with the pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic causes of jaundice (with “hepatic” meaning: relating to the liver).
During the webinar, Dr Rajesh shed light on the post-hepatic causes of jaundice. All the deets on that right below…
Post-hepatic causes of jaundice
Aka obstructive jaundice, as there’s obstruction to the flow of bile or bilirubin after the liver, causing bilirubin to accumulate and increase over time, eventually leading to jaundice. Among the causes of obstructive jaundice are:
- Gallstone disease
- Pebble-like gallstones lodge in the bile duct, which is one of the parts where bilirubin would flow through. This causes a blockage in the bilirubin flow and makes bilirubin spike.
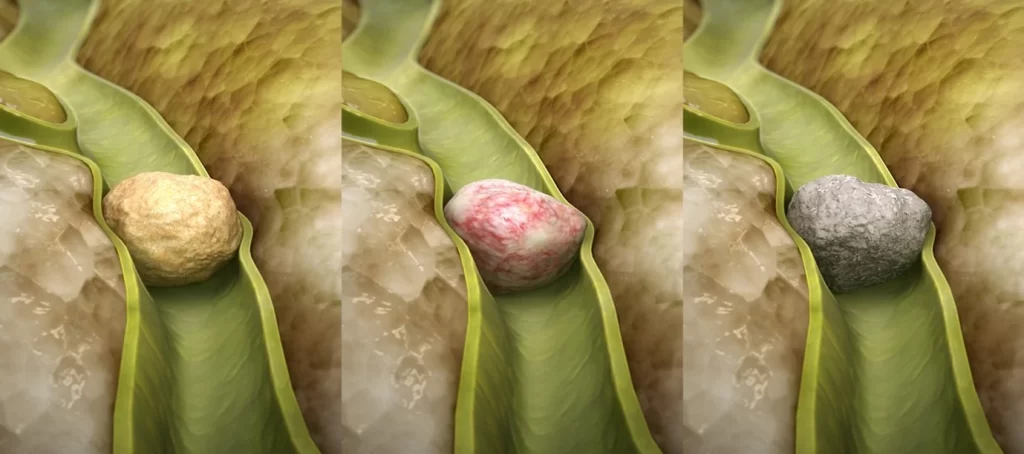
Pebble-like gallstones forming a blockage in the bile duct
- Pancreatic cancer
- Since the pancreatic duct is near the bile duct, pancreatic cancer will block the bile duct as well, thus causing an obstruction to bilirubin flow. Similarly, this leaves bilirubin to accrue to a point where jaundice is developed, due to its higher-than-usual amount.
- Bile duct cancer
- Another factor for blockage along the bile duct, thereby bringing disruption to bile or bilirubin flow, which would then bring on jaundice.
Of course, there are also pre-hepatic and hepatic jaundice causes. To understand more, speak to our consultants here.
Other risk factors for jaundice
- Diabetes
- Being overweight
- Eating a high-fat, low-fibre diet
- Smoking and excessive alcohol drinking
- Family history of gallstones
- Had pancreas inflammation or infection before
- Female
- Aging
- Exposed to industrial chemicals
Now…what are the symptoms?
According to Dr Rajesh during the webinar, symptoms of jaundice can be manifested in various ways, they include:
- Yellow eyes and skin
- Itchy skin
- Dark urine and pale stool
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Throwing up
- Diarrhea
- Malignant weight loss
- Fever
So, how do we treat jaundice?
To tailor the best solution to the problem, certain tests or investigations will be carried out first to discover the root causes of jaundice.
Preliminary tests to find out a rough idea of what’s happening:
- Blood tests
- Urinalysis (a test of your urine)
Advanced tests to probe further into the fundamental causes:
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound (US) abdomen, CT scan, PET-CT, and MRI
- Endoscopy
Once the underlying causes of jaundice are identified, the right treatments will then be conducted to address the causes. Since jaundice can be caused by gallstone disease, pancreatic cancer, and bile duct cancer as stated above, Dr Rajesh has shared with us the respective treatment available for these three causes. Let’s dig in!
- For gallstone disease…
- The harmful gallstones can be removed with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
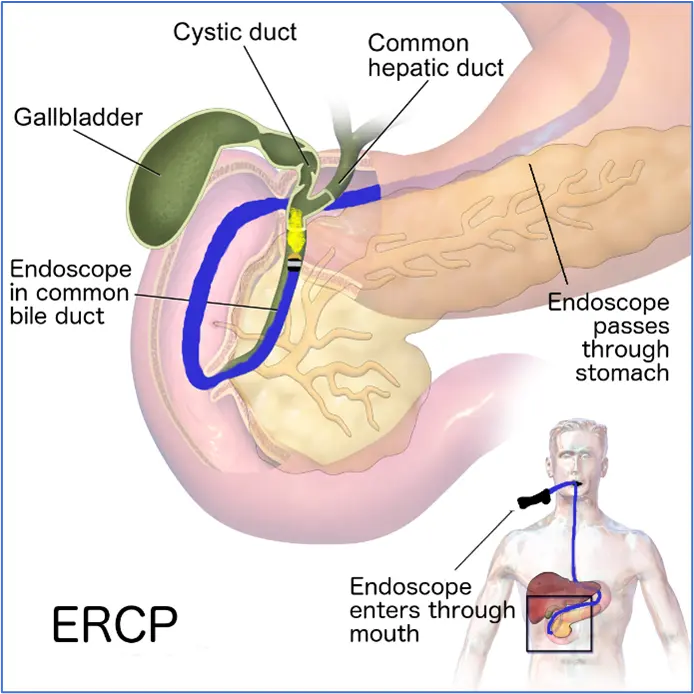
Gallstone removal from the bile duct via ERCP
What about ways to prevent jaundice?
Jaundice prevention starts from our lifestyle habits. One can avoid facing the onset of jaundice by:
- Having a healthy diet
- Avoid eating raw seafood
- Exercise from time to time
- Say no to smoking
- If you are taking alcohol, take it only in moderation
- Avoid being exposed to industrial carcinogens
TL; DR: Bilirubin in our body going through the roof is the main reason why jaundice happens. So, when it comes to yellow eyes, dark urine, etc., it all boils down to the amount of bilirubin there is inside us. To learn about jaundice in depth, watch and listen to Dr Rajesh’s full webinar on jaundice here, or contact our consultants for professional health advice.












